How to find the right seal for your hydraulic or pneumatic cylinder application
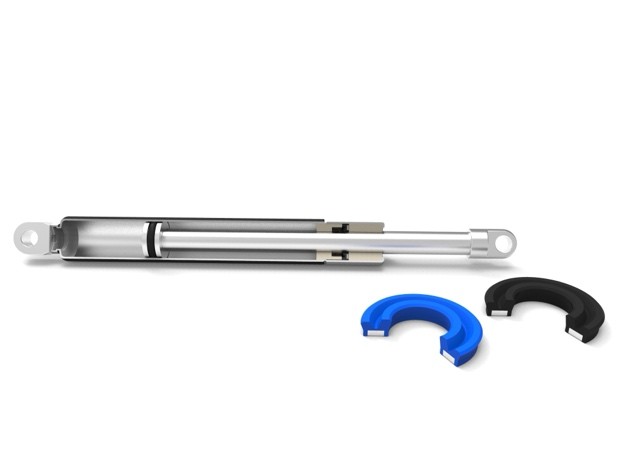

Seal components are among the smallest components in hydraulic and pneumatic systems, but they are extremely important for efficiency, durability, and productivity in construction machinery, agricultural machinery, mining, plastics machinery, and factory automation. If the sealing system is not suitable for the application, this can have major economic consequences for the machine operator. Machine manufacturers must consider many factors when choosing a sealing system and rely on reliable partners. This article summarizes the most important aspects.
Sealing systems: Focus on sustainability and environmental compatibility
The selection of suitable seals for hydraulic and pneumatic systems is influenced by global trends that are changing both technical requirements and regulatory conditions. In hydraulics, biodegradable fluids such as HEES (hydraulic oils based on saturated synthetic esters) or HETG (plant-based) are increasingly being used, especially in ecologically sensitive areas such as agriculture and forestry. These fluids place completely different demands on the sealing material than conventional mineral oils. Classic materials such as NBR (nitrile rubber) are often insufficient here, which is why higher-quality materials such as FKM (fluorinated rubber) or special PU (polyurethanes) with adapted chemical resistance are required.
In pneumatics, the ever-increasing dynamics of processes in factory automation in pneumatic applications are in turn resulting in higher cycle rates and shorter cycle times. This is accompanied by a significantly increased load on the sealing systems. To avoid stick-slip effects (jerky movements due to excessive static friction), the seals must have very low friction and high wear resistance. Materials such as PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) or coated elastomers with slip-modified surfaces are increasingly being used here.
In mobile hydraulics, the electrification of machines is placing ever higher demands on drive systems and thus also on sealing systems. More compact, energy-efficient, and often quieter hydraulic systems are required to ensure optimal synergy effects with the electrified drives. This results in requirements for seals with minimal leakage, low friction losses, and optional integration into digital condition monitoring systems. Machines that are used worldwide must function reliably under highly diverse environmental conditions and in compliance with different country-specific standards.
For machine designers, these conditions mean that the choice of sealing elements is anything but trivial. Reliable partners who can offer expert advice and a comprehensive portfolio of sealing solutions are a must for OEMs who want to integrate reliable and robust hydraulic and pneumatic systems.
Economic and reputation-damaging consequences of leaks
Leaks and the associated consequences have various, sometimes serious, consequences for machine operators and manufacturers.
If mineral oil-based liquids enter ecosystems or groundwater, this causes enormous environmental damage and must therefore be avoided at all costs.
Such incidents can have significant economic consequences for the companies responsible. The release of oils and gases into the environment can result in fines running into millions. For medium-sized machine operators, such sums can, under certain circumstances, threaten the continued existence of their business.
For machine manufacturers, on the other hand, extensive leaks damage their reputation and can have a negative impact on sales of the machines and equipment affected. In any case, however, leaks lead to maintenance and machine downtime. Depending on the area of application, this unplanned downtime can also result in significant economic damage.
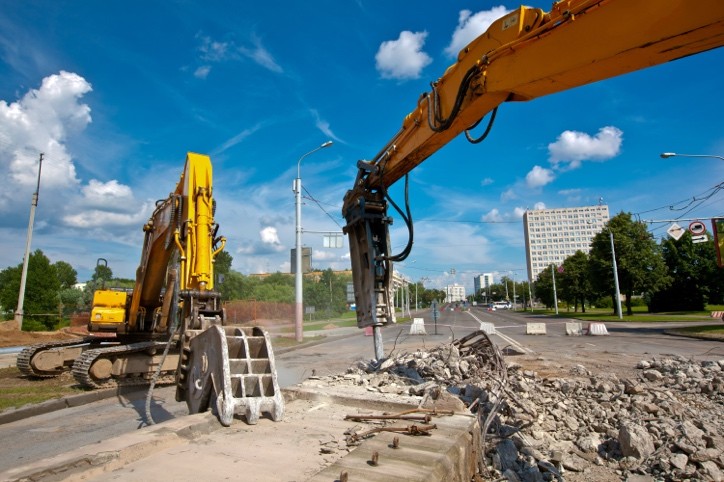

Typical examples can be found in the construction and agricultural industries in particular. If a road paver on a construction site is unexpectedly shut down, the delivered asphalt may, in the worst case, not be able to be processed within the specified temperature range. Delays in the construction process can result in severe contractual penalties or claims for damages.
If a combine harvester breaks down in the middle of the harvest, this can be expensive for the farmer concerned. The delay can lead to crop losses or quality losses, for example due to mold growth as a result of excessive moisture.
Although leaky pneumatic systems have no negative impact on the environment, they do lead to production problems and, in any case, to increased costs for the machine operator. Leaks can, for example, lead to inconsistent behavior of pneumatic grippers and thus to production downtime due to necessary maintenance. Escaping compressed air also represents an enormous cost factor. Leaks must therefore be avoided for a variety of reasons. Sealing systems are crucial for avoiding costs and maintaining image.
General aspects when choosing a seal

Choosing the right seal is therefore crucial for the performance, reliability, and ease of maintenance of hydraulic and pneumatic cylinders. Incorrect material selection, insufficient media resistance, or unfavorable installation conditions can lead to failures, leaks, or premature wear. The following factors must always be taken into account:
• Different loads and environmental conditions
Hydraulic and pneumatic cylinders operate under a wide variety of conditions. Extreme weather conditions, high pressure peaks, high temperatures, the dynamics of the process, or contact with aggressive media are just a few of the aspects that machine and subsystem designers must take into account.
• Media resistance
Different fluids, different properties: classic mineral oils, synthetic fluids, biodegradable oils, or compressed air place a wide variety of demands on the sealing materials used.
• Friction and wear
Excessive friction leads to energy losses and can cause stick-slip effects. At the same time, the seal must be wear-resistant enough to withstand high cycle counts, otherwise there is a risk of leakage.
• Surface roughness values and quality
Seals work in contact with sliding or moving surfaces. If the surface is too rough, this can accelerate wear, lead to leaks or destroy the seal. If, on the other hand, the seal surface is too smooth, this prevents the necessary lubricating film from forming or can lead to stick-slip effects. It is therefore important to machine the seal optimally to ensure the best possible roughness value and surface quality. To achieve this, micro and macro structures are incorporated during production.
• Material selection
Seals for hydraulic and pneumatic applications are available in various materials. These have individual advantages, as shown in the overview below.
| Material | Properties | Typical application |
|---|---|---|
| NBR (nitrile rubber) | Good oil resistance, limited temperature resistance | Standard hydraulic cylinder applications |
| FKM | Excellent chemical and temperature resistance | Applications with hot fluids, e.g., plastic machines |
| PU (polyurethane) | Highly abrasion-resistant, mechanically stable | High-pressure applications, e.g., in construction machinery |
| PTFE | Very low friction, media-resistant | Dynamic applications with high pressure and high speeds |
What matters when it comes to seals for hydraulic cylinders
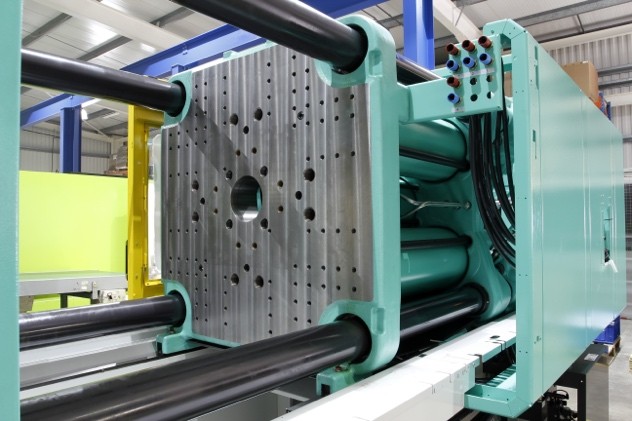


Hydraulic systems are used in various industries due to their numerous advantages, including low maintenance, easy handling, long service life, and high power density. In these systems, hydraulic cylinders are responsible for functions such as pressing, lifting, and pushing. The most common areas of application include:
- Agriculture
- Mining
- Construction machinery
- Hydraulic presses
- Iron and steel industry
- Mobile equipment
Selecting the right seal requires a comprehensive understanding of the system: pressure, medium, dynamics, installation space, and operating conditions must all be considered together. These key aspects determine the performance and service life of a hydraulic system. This is the only way to avoid leaks, energy losses, and premature wear.
Design engineers of mobile machines or stationary hydraulic systems should therefore pay attention to the following when selecting seals for their cylinder applications.
• High pressure resistance
Hydraulic cylinders operate at working pressures of 100–400 bar, and pressure peaks in high-pressure applications can be significantly higher. This extreme pressure can lead to extrusion, i.e., the sealing material being pressed out of the sealing gap. The sealing material must therefore be designed for these pressure peaks. Support or back-up rings can be used for this purpose, for example.
• Temperature resistance and media compatibility
Ambient temperatures can fluctuate extremely, especially in mobile machines. Hydraulic systems must operate reliably at temperatures ranging from a low of –40 °C to a desert heat of +50 °C. Added to this is the hydraulic oil temperature of up to +150 °C. Given the increasingly varied compositions, from mineral oil to synthetic ester-based fluids, the hydraulic fluid also has a major influence on the seal used. The sealing material used must be able to withstand both this wide temperature range and the potentially aggressive media. Using the wrong material can lead to swelling, cracking, or hardening of the seal, thereby negatively affecting its sealing performance.
• Seal geometry and abrasion resistance
The seal geometry has a direct influence on the friction generated in the system. Excessive friction increases energy consumption, can lead to stick-slip effects (jerky start-up), and heat up the components. It therefore has a direct influence on the productivity and efficiency of the machine . High-performance solutions therefore rely on multi-lip seals or asymmetry in the seal geometry to maintain the lubricating film optimally and reduce friction. This is because piston and rod seals in hydraulic cylinders are dynamically loaded over millions of strokes and must still ensure a uniform seal at all times. The oil film between the seal and the mating surface is crucial here. The preload acting on the seal must also be selected correctly to avoid friction and leakage.
Given the enormous forces acting in hydraulics, lateral forces must be prevented from acting on the seal. Otherwise, this could lead to uneven sealing and wear. Guide rings are used for this purpose to absorb these forces.
Last but not least, mobile machines in particular operate in dusty or dirty environments. The sealing system has the task of keeping these dirt particles out of the cylinder drive. Solid particles in the cylinder system can affect the stroke quality, damage the rod surface, and lead to leaks and wear by disrupting the lubricating film. Combinations of rod seals and wipers, usually made of PU or PTFE, can be an effective means of preventing contamination. In the most demanding applications, the use of closed sealing systems or multiple sealing systems may be necessary.
For maintenance purposes, ease of installation should also be taken into account, especially in applications where long service intervals and machine downtime can have major economic consequences.
• Surface quality of the mating surfaces
In hydraulic applications, too, the interaction between the seal and the piston rod or cylinder bore is a decisive factor for reliable sealing. For the sealing contact surface, e.g., piston rod or shaft area, ISO 6194-1 requires, for example, a roughness of Ra = 0.2 µm to 0.63 µm and a maximum peak value of Rmax = 0.8 µm to 2.5 µm for hardened and ground shaft surfaces.
For the housing bore, the surface must not exceed Ra ≤ 3.2 µm or Rmax ≤ 12.5 µm – again with reference to ISO 468.
What is important for seals for pneumatic cylinders

As already mentioned, the environmental conditions and requirements for hydraulic and pneumatic sealing elements differ significantly. What is particularly important for pneumatic seals?
Pneumatic cylinders operate at low pressures, usually up to a maximum of 10 bar. The movements of the cylinders are often fast, short, and high-frequency. Even slight static friction can lead to stick-slip. Pneumatic seals must therefore be easy to slide, e.g., through the use of PTFE or specially coated PU. Compressed air often contains little lubricant or is completely dry ( ), e.g., in clean room applications. The sealing materials must therefore function even without lubrication, otherwise there is a risk of rapid wear or seal failure. The seal must also be compatible with compressed air additives such as condensate oil, drying agents, or cleaning gases. FKM materials have proven themselves for this purpose.
Unlike in hydraulics, where the system pressure additionally activates the sealing effect, pneumatic seals must seal even without these pressure effects. Therefore, good preload of the seal or special geometry is necessary for sealing in the low-pressure range.
To prevent contamination by particles, which can always accumulate in pneumatic systems, and subsequent leaks, sealing systems with wipers or integrated filters may need to be used.
Pneumatic cylinders often complete millions of cycles – e.g., in packaging machines or in automation. Therefore, seals in these applications must be low-wear, thermally stable, and dynamically resilient.
In pneumatic systems in particular, unsuitable surface roughness (especially at the groove bottom) can lead to leaks. In pneumatic systems, it is recommended that the dynamic working surface of the rod has a hardness between 55 and 60 HRC and is hard chrome-plated with 25 to 40 μm. It is recommended that the bore surfaces be machined using processes such as honing, grinding, and hard anodizing.
Roughness Rmax is the most important component of the surface quality specification according to DIN ISO 4287. Rmax is the largest single roughness depth of the individual measuring sections. Rz corresponds to the arithmetic mean of the individual roughness depths of all individual measuring sections. To evaluate the dynamic running surface, the coefficient should be calculated from the individual measured values of the roughness depth Rp and the measured roughness Rz. Rp refers to the distance from the center line to the highest profile peak within the individual measuring section. Profiles with Rp/Rz < 0.5 are a suitable value for pneumatic applications in terms of wear and service life of elastomer sealing elements. Rp/Rz > 0.5 leads to premature wear of sealing elements in open profiles.
Source:
- Kastas: https://www.kastas.com/en/knowledge-bank/pneumatic-technical-information
- Zeiss: https://pages.zeiss.com/rs/896-XMS-794/images/DE_60_050_004I_Oberflaeche_A0.pd
The right sealing solution for your application
Kastas Sealing Technologies, based in Izmir, Turkey, has been one of the leading partners of premium machine manufacturers for more than 40 years. The experienced R&D team develops customized solutions for the most demanding applications, from standard solutions to customer-specific special solutions. Kastas has all the necessary expertise in-house to rethink sealing elements from the ground up. With 40,000 m2 of manufacturing facilities, the company can carry out all processes in-house, from product design and raw material procurement to production. Before producing prototypes, the Kastas development team relies on comprehensive simulations, such as finite element analysis, to reduce development costs and create the best possible solutions. The in-house development of elastomer composites also contributes to this, enabling the company to meet the ever-increasing demands of fluid technology. The in-house testing center allows Kastas to comprehensively test its sealing solutions for hydraulic and pneumatic pistons and rods for leakage, friction, wear, extrusion, temperature resistance, and stick-slip effect under high and low pressure before they are placed on the market. The Kastas product portfolio includes rod and piston seals for all hydraulic and pneumatic cylinder applications, static seals, wipers, guide elements, O-rings, and rotary seals. In total, more than 15,000 variants are available for use in construction machinery, agricultural machinery, mobile hydraulics, industry, mining, and metalworking. Click here to view the Kastas product portfolio: https://www.kastas.com/en/products
With SmartSeal, Kastas offers a production service that can respond to urgent and special customer requirements within 24 hours. State-of-the-art CNC systems are used to produce customer-specific sealing solutions within minutes.
The SmartSeal service also includes the customer-specific manufacture of semi-finished products for seal production. SmartSeal Material Solutions produces high-performance polymer semi-finished products, mainly from PTFE, polyurethane, and composite materials, in a wide range of sizes and material variants using high-quality raw materials.
More about the SmartSeal service: https://www.kastas.com/en/smartseal-en
To make the procurement of sealing solutions even more customer-friendly, Kastas offers its own online shop, seal-Link. Using an intelligent search and intuitive filter functions, interested parties can quickly and easily find the right seal for their application, as well as information on stock availability and product prices. Alternatively, a variety of categories are available to provide a comprehensive overview of the various products.
Click here to visit the seal-Link online shop: https://www.seal-link.com/en-US/
Manufacturers of construction machinery, agricultural machinery, plastics machinery, factory automation systems, and mining equipment will find Kastas Sealing Technologies to be a competent and experienced partner that impresses with its expertise in research and development as well as production. Design engineers of these machines can rely on advice from experienced sales engineers to find the best sealing solution for their application. Kastas has an international sales network in 80 countries. Kastas Europe, based in the north of Hamburg, has its own distribution center that stocks the entire product range and guarantees Europe-wide delivery within 24 hours.
Application examples Construction machinery

Construction machinery is highly complex and must deliver high performance under extreme environmental conditions (heat, cold, dust, dirt, moisture) throughout decades of service life. To ensure the necessary power density, they operate with high-pressure hydraulic systems. This requires sealing elements with high sealing performance, characterized by perfect static and dynamic sealing, low friction, resistance to extrusion, and a long service life.
By using high-performance materials and composites that withstand high and low temperatures and ensure media compatibility, Kastaş Sealing Technologies designs and develops innovative and reliable solutions that meet these requirements.
For more information on Kastas' industry solutions, please visit: https://www.kastas.com/en/documents-literature
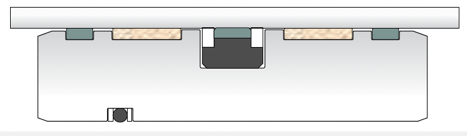
• Sealing system for wheel loaders and excavators

Konfiguration K05-K33-K35-K75-K84
- Excellent sealing performance
- Long service life
- Good scraping performance and tightness thanks to the sealing lip of the K05
- Good price-performance ratio
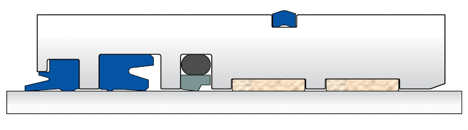
K07-K31-K29-K75-K84
- Best sealing performance even under pressure peaks
- Simple groove design and quick installation
- Best sealing performance even at high or low pressure
- High abrasion resistance
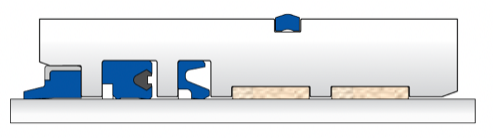
K518-K75-K81
- Best sealing properties
- Excellent guiding properties
- Long service life
- Economical sealing system solution and easy installation
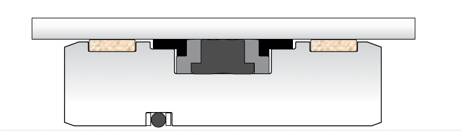
K19-K75-KBT-K81
- Excellent sealing and guiding properties
- Simple groove design and quick installation
- Very good sealing solution for high pressures and speeds